Plugins
Overview
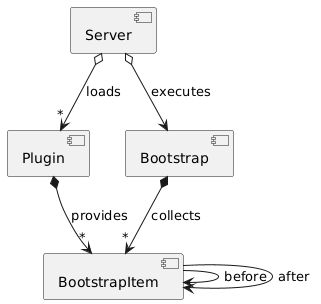
Plugin is a set of functionality, i.e. Java classes packed into one or multiple JAR files. The Server loads and initializes such JARs.
Loading and initialization steps
Loading and initializing are two separate steps of the process.
At the first step a part of the server, the PluginLoader scans the JAR files for implementations of IPlugin. It uses PluginCreator to instantiate the Plugin by passing the instance of IBootstrap to it’s constructor. The load() method of each Plugin is called here.
In it’s load() method the Plugin adds it’s own IBootstrapItem into the IBootstrap known to him. The IBootstrapItem gives the name of the part of the functionality provided by the plugin and allows to declare dependencies from the other bootstrap items using the after() and before() methods. Finally the sequence of the bootstrap items according to the dependencies is constructed and their executeProcess() is called. This is the second step of the initialization.
Sample plugin
Let create a sample plugin.
public class SamplePlugin implements IPlugin
Bootstrap reference
It must contain a reference to Bootstrap provided during initialization process.
private final IBootstrap<IBootstrapItem<String>> bootstrap;
The Bootstrap must be injected into the plugin’s constructor.
public SamplePlugin(final IBootstrap<IBootstrapItem<String>> bootstrap) {
this.bootstrap = bootstrap;
}
Load method
You have to define the load() method.
@Override
public void load() throws PluginException {}
In the method at the first you should declare the BootstrapItem provided by your plugin.
IBootstrapItem<String> item = new BootstrapItem("SamplePlugin");
Here you declare that your item must be initialized after initialization of 'IOC' item.
item.after("IOC");
Initialization callback
Then you define your plugin initialization code. For example, let register some new strategy in IOC.
item.process(() -> {
try {
IKey key = Keys.getKeyByName("new SampleClass");
IOC.register(
key,
// it's the initialization action of our plugin
new CreateNewInstanceStrategy(
(args) -> new SampleClass((String) args[0])
)
);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("SamplePlugin initialized");
});
Registering the callback
Finally you should add your bootstrap item into Bootstrap:
bootstrap.add(item);
How plugins are loaded
On the server side the loading of the plugin may looks as the following.
Bootstrap
The server initializes the Bootstrap to handle the initialization sequence.
IBootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
PluginCreator
Also it uses PluginCreator to find and call the correct constructor of IPlugin.
IPluginCreator creator = new PluginCreator();
PluginLoaderVisitor
A IPluginLoaderVisitor is necessary to track plugins loading process.
IPluginLoaderVisitor<String> visitor = new SamplePluginVisitor();
ModuleManager
Because the plugin jars can be located in different directories and can be added dynamically, the special object named ‘module’ needs to be created to store each plugin inside the server.
ModuleManager.addModule(pluginId, pluginName, pluginVersion);
PluginLoader
Then this ‘module’ for plugin must be setup as current and PluginLoader is created. The second constructor’s parameter is the code to load each plugin.
ModuleManager.setCurrentModule(ModuleManager.getModuleById(pluginId));
IPluginLoader<Collection<IPath>> pluginLoader = new PluginLoader(
ModuleManager.getCurrentClassLoader(),
(t) -> {
try {
IPlugin plugin = creator.create(t, bootstrap);
plugin.load();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not create instance of IPlugin", e);
}
},
visitor
);
Loading
The server scans the collection of jar files for IPlugin instances.
Collection<IPath> fileCollection = new ArrayList<>();
fileCollection.add(new Path("libs/SamplePlugin.jar"));
fileCollection.add(new Path("libs/IocPlugin.jar"));
pluginLoader.loadPlugin(fileCollection);
Initialization
And then calls the initialization code of BootstrapItems in the sequence according to their dependencies.
bootstrap.start();
Initialization order
In this example, when we have two plugins: ‘SamplePlugin’ following after ‘IOC’ — the loading and initialization sequence is like this:
SamplePlugin.load(), registers bootstrap itemIOCPlugin.load(), registers bootstrap item- initialization code of bootstrap item of ‘IOC’ plugin
- initialization code of bootstrap item of ‘SamplePlugin’ because it asked to be after ‘IOC’
Note the order of first two steps is not defined, while the order of execution of bootstrap items is defined by their dependencies.
Code of the example
You can check the full source codes of this example here.